Keep the Heat Flowing: Proven Methods for Heat Exchanger Maintenance
In Summary
Heat exchanger maintenance involves regular inspections, cleaning, and repairs to ensure optimal performance and prevent any potential issues. This process helps maintain the efficiency and longevity of the heat exchanger, which is crucial for various industrial and residential applications.
Understanding Heat Exchangers
To properly maintain your heat exchanger, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what a heat exchanger is and how heat transfer mechanisms work.
What is a Heat Exchanger?
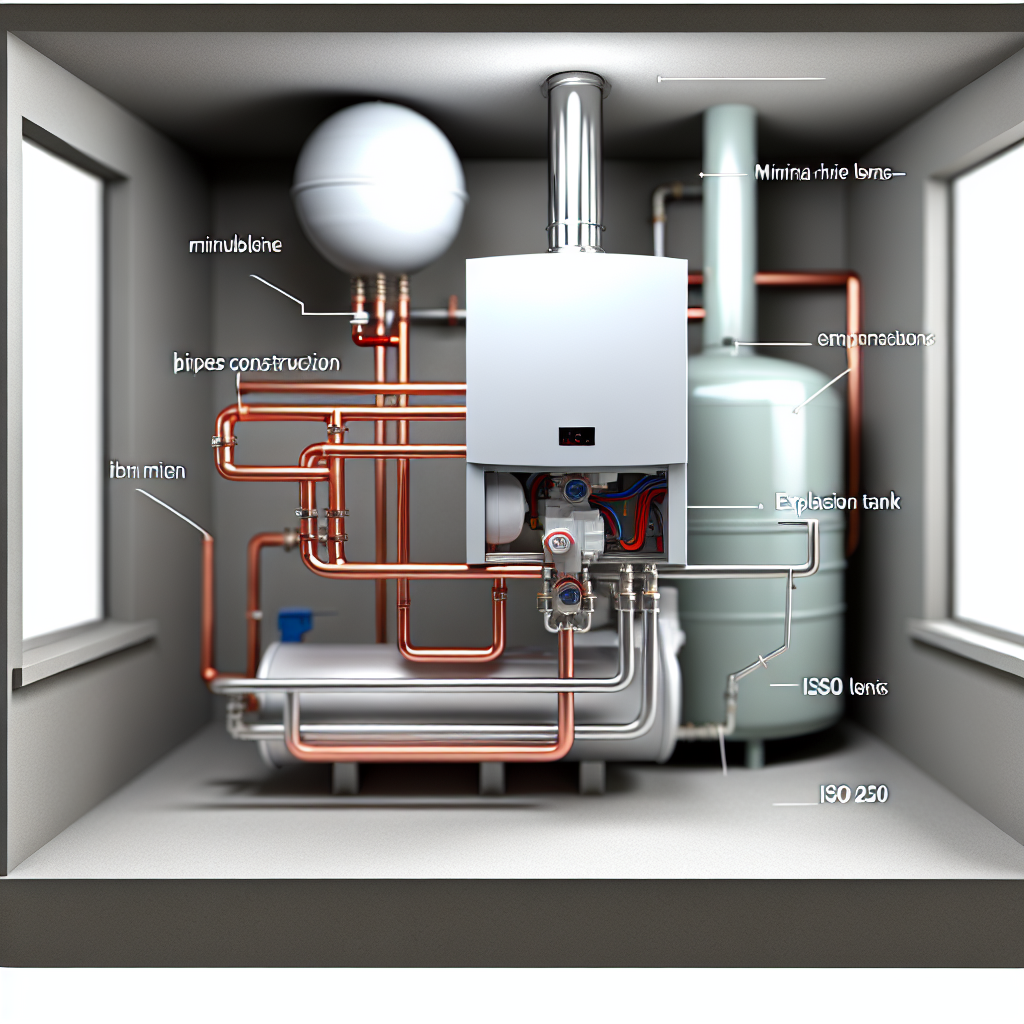
A heat exchanger is a device designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids of different temperatures. It plays a crucial role in various heating and cooling applications, including HVAC systems, refrigeration systems, and industrial processes. The primary purpose of a heat exchanger is to efficiently transfer thermal energy from one fluid to another, without the fluids coming into direct contact with each other.
Heat exchangers are commonly used to heat or cool air, water, or other fluids by utilizing the principles of heat transfer. They consist of a network of tubes or plates through which the hot and cold fluids flow. The heat is transferred from the hot fluid to the cold fluid through the walls of the tubes or plates.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Heat transfer in a heat exchanger occurs through three main mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat energy through direct contact between solids or between a solid and a fluid. It follows the principle that heat flows from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature. The rate of heat transfer by conduction depends on factors such as the thermal conductivity of the material, the cross-sectional area, the temperature difference, and the thickness of the material.
Convection: Convection involves the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid, such as air or water, that has been heated. When the hot fluid comes into contact with a colder surface, it transfers heat energy to the surface. The rate of heat transfer by convection is influenced by factors such as the convective heat transfer coefficient, the surface area, and the temperature difference between the surface and the fluid.
Radiation: Radiation is the transfer of heat energy through the emission of electromagnetic waves from a heated surface or object. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium to transfer heat. The rate of heat transfer by radiation is determined by factors such as the emissivity coefficient of the material, the surface area, and the temperature difference between the hot object and its surroundings.
Understanding these heat transfer mechanisms is crucial for assessing the performance and efficiency of your heat exchanger. By comprehending how heat is transferred within the system, you can identify potential issues and implement proper maintenance practices to ensure optimal heat exchange.
In the following sections, we will explore the importance of heat exchanger maintenance, factors that affect heat exchanger performance, maintenance practices, signs of heat exchanger issues, safety considerations, and different types of heat exchangers.
Importance of Heat Exchanger Maintenance
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your heat exchanger, regular maintenance is essential. Neglecting maintenance can lead to a range of problems that can impact both the efficiency and safety of your heat exchanger. In this section, we will discuss the common problems associated with heat exchangers and the potential dangers of heat exchanger failure.
Common Problems with Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers, particularly those in furnaces, are susceptible to various issues. One of the most common problems is heat exchanger failure, accounting for approximately 75% of all heating system failures. The failure can occur due to factors such as age, fouling, corrosion, and mechanical stress.
Age is a significant factor in heat exchanger failure, with most problems occurring in units that are 15-20 years old . As the heat exchanger ages, it becomes more prone to cracks, leaks, and other forms of damage. This can compromise its ability to transfer heat effectively and may result in reduced performance and efficiency.
Fouling is another major issue that affects heat exchangers. Over time, dirt, debris, scale, and other deposits can accumulate on the heat exchanger surfaces. This fouling restricts airflow and decreases the efficiency of heat transfer. In fact, fouling can decrease operating efficiency by up to 30% .
Corrosion is yet another concern for heat exchangers. Exposure to moisture, chemicals, and certain operating conditions can cause corrosion, leading to leaks and decreased performance. Regular maintenance and appropriate corrosion prevention measures are crucial to mitigate this problem.
The Dangers of Heat Exchanger Failure
Failure to address heat exchanger problems can have serious consequences, including safety hazards. One of the most significant risks associated with heat exchanger failure is the potential release of carbon monoxide (CO) gas into the living space. A cracked or damaged heat exchanger can allow combustion gases, including CO, to escape into the air that circulates within the home. Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that is odorless, colorless, and potentially lethal. It poses a significant health risk to individuals exposed to it.
To ensure the safety of your household, it’s crucial to address heat exchanger issues promptly. Regular maintenance, including inspections and cleaning, can help identify and rectify problems before they escalate. By addressing common problems and performing necessary repairs or replacements, you can maintain the efficiency and safety of your heat exchanger.
In the next section, we will explore the factors that can affect the performance of heat exchangers, providing insights into how regular maintenance can address and prevent these issues.
Factors Affecting Heat Exchanger Performance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your heat exchanger, it’s important to understand the factors that can affect its efficiency. Three key factors that impact heat exchanger performance are age and lifespan, fouling and decreased efficiency, and corrosion and tube leaks.
Age and Lifespan
Age is a significant factor in heat exchanger failure. Most problems occur in units that are 15-20 years old, according to 333 Help. Over time, wear and tear can degrade the performance and structural integrity of the heat exchanger. Components may become worn or weakened, leading to decreased efficiency and potential failure.
Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to identify signs of aging and address potential issues before they escalate. By monitoring the age of your heat exchanger and following recommended maintenance practices, you can extend its lifespan and ensure optimal performance.
Fouling and Decreased Efficiency
Fouling is a major cause of heat exchanger failures and can decrease operating efficiency by up to 30%, as noted by AmmoniaKnowHow. Fouling refers to the accumulation of deposits on the heat exchanger surfaces, such as scaling, sediment, or biological growth. These deposits act as insulators, reducing the heat transfer efficiency of the exchanger.
The specific fouling mechanisms can vary depending on the application and the substances involved. Common causes of fouling include mineral deposits, biological growth, and particulate matter in the fluid being processed. Regular cleaning and maintenance, as well as using appropriate heat exchanger cleaning methods, are essential to prevent fouling and maintain optimum heat transfer performance.
Corrosion and Tube Leaks
Corrosion is another critical factor that can impact heat exchanger performance. Condensation of corrosive gases, exposure to aggressive chemicals, or improper pH levels in the process fluid can lead to pitting corrosion in heat exchangers, as outlined by AmmoniaKnowHow. Corrosion weakens the structural integrity of the exchanger and can result in leaks or rupture.
Tube leaks are a common issue in heat exchangers and can have serious consequences. They can lead to cross-contamination of fluids, loss of product, and even pose safety hazards. Regular inspection and maintenance, including checking for signs of corrosion and addressing any leaks promptly, are essential to ensure the integrity and functionality of the heat exchanger.
Failure to properly address and repair heat exchanger issues can result in costly shutdowns, production losses, and potential safety risks. It is crucial to have a proactive maintenance plan in place, including routine inspections, cleaning, and addressing any signs of aging, fouling, corrosion, or leaks. By prioritizing heat exchanger maintenance, you can maximize its performance, efficiency, and lifespan.
Heat Exchanger Maintenance Practices
To keep your heat exchanger running smoothly and efficiently, regular maintenance is essential. By following these maintenance practices, you can help prevent potential issues and ensure the longevity of your heat exchanger.
Annual Inspection and Cleaning
One of the most crucial maintenance tasks for a heat exchanger is an annual inspection and cleaning. Over time, dirt, debris, and other contaminants can accumulate on the surfaces of the heat exchanger, leading to reduced efficiency and potential problems . It is recommended to have a professional HVAC technician perform this inspection to ensure thoroughness and accuracy.
During the inspection, the technician will assess the condition of the heat exchanger, checking for any signs of damage, leaks, or corrosion. They will also clean the surfaces of the heat exchanger to remove any dirt, debris, or fouling that may have accumulated . Regular cleaning helps maintain optimal heat transfer and prevents the buildup of contaminants that can hinder performance.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
In addition to annual inspections and cleanings, following a preventive maintenance checklist can help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of your heat exchanger. Here are some key tasks to include in your preventive maintenance routine:
- Regularly inspect the heat exchanger for any signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage. Promptly address any issues to prevent further complications .
- Clean the surfaces of the heat exchanger regularly to remove dirt, debris, and fouling that can hinder heat transfer .
- Replace any damaged or worn-out components, such as seals or gaskets, to maintain the integrity of the heat exchanger .
- Ensure proper airflow around the heat exchanger by keeping the surrounding area free from obstructions. Adequate airflow is crucial for optimal heat exchange and preventing overheating.
By following a preventive maintenance checklist, you can stay proactive in addressing any potential issues and maximizing the performance of your heat exchanger.
Monitoring Performance and Temperature
Regularly monitoring the performance and temperature of your heat exchanger is another important aspect of maintenance. Keep an eye out for any signs of reduced efficiency, such as decreased heating or cooling output, longer operating times, or unusual noises. These may indicate underlying issues with the heat exchanger .
Additionally, monitor the temperature of the heat exchanger to ensure it is operating within the recommended range. Temperature deviations could signify problems with heat transfer or flow, which should be investigated promptly to prevent further damage or inefficiency.
By staying vigilant and proactive in monitoring the performance and temperature of your heat exchanger, you can detect and address any issues early on, potentially avoiding costly repairs or replacements.
Regular maintenance practices, including annual inspections and cleanings, following a preventive maintenance checklist, and monitoring performance and temperature, are essential for ensuring the optimal functioning and longevity of your heat exchanger. By taking these steps, you can prevent common problems, maximize efficiency, and enjoy uninterrupted comfort in your home.
Signs of Heat Exchanger Issues
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your heat exchanger, it’s important to be aware of potential issues that may arise. By recognizing the signs of heat exchanger problems, you can take timely action to address them and prevent further damage. Here are some key signs to watch out for:
Reduced Performance and Efficiency
If you notice a decline in the performance and efficiency of your heat exchanger, it may be an indication of underlying issues. Reduced heat transfer efficiency can result from various factors, such as fouling or scaling that accumulates on the heat exchange surfaces. This buildup can impede the heat transfer process, leading to decreased performance and increased energy consumption.
Monitoring the temperature difference across the heat exchanger can provide valuable insights into its efficiency. A significant increase in temperature difference compared to normal operation may be a sign of fouling or other issues affecting heat transfer. If you observe a decline in performance, it’s crucial to address the problem promptly to restore the heat exchanger’s optimal functioning.
Leaks and Corrosion
Leakage is a serious issue that should never be ignored. If you notice any signs of leakage, such as water or fluid seeping from the heat exchanger, it indicates a breach in the system. Leaks can occur due to erosion or corrosion of the tubes, which compromises the integrity of the heat exchanger. Continuing to operate a heat exchanger with leaks can lead to further damage and potentially hazardous situations.
Corrosion is another concern when it comes to heat exchanger maintenance. Over time, exposure to the operating environment can cause corrosion on the surfaces of the heat exchanger, particularly if it is made of materials susceptible to corrosion. Corroded components can weaken the structure and cause leaks. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to identify signs of corrosion early on and take appropriate measures to prevent further deterioration.
Warning Signs to Look Out For
Apart from performance issues, there are several warning signs that may indicate problems with your heat exchanger. Pay attention to the following indicators:
- Unusual noises: If you hear strange sounds, such as rattling or banging, coming from the heat exchanger, it could be a sign of loose components or excessive vibration. These issues should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage.
- Uneven heating or cooling: If your heat exchanger is not providing consistent heating or cooling, it may indicate problems with the distribution of heat. This can be caused by issues like blocked tubes or insufficient fluid flow.
- Unpleasant odors: Foul smells emanating from the heat exchanger could be a sign of contamination or bacterial growth. It’s important to investigate and rectify the source of the odor to maintain a safe and healthy environment.
- Increased energy consumption: If you notice a significant increase in energy usage without any apparent explanation, it could be attributed to reduced efficiency or other issues with the heat exchanger. Monitoring energy consumption patterns can help identify abnormalities and guide maintenance efforts.
Regular inspection and maintenance of your heat exchanger, including cleaning, monitoring performance, and temperature measurements, are vital to detect these signs early on and prevent further complications. If you encounter any of these issues or suspect problems with your heat exchanger, it’s advisable to consult a professional for a thorough assessment and appropriate repairs.
Remember, ensuring the proper functioning of your heat exchanger not only improves energy efficiency but also contributes to the safety and comfort of your home.
Safety Considerations for Heat Exchangers
When it comes to maintaining your heat exchanger, ensuring safety is of utmost importance. Heat exchangers, particularly those in furnaces, can pose certain risks if not properly maintained. In this section, we will discuss two key safety considerations: carbon monoxide risk and proper combustion and ventilation.
Carbon Monoxide Risk
A cracked heat exchanger can lead to the release of carbon monoxide into your home, which is a poisonous gas that can be deadly . Carbon monoxide is a byproduct of the combustion process, and a malfunctioning heat exchanger can allow this gas to escape into your living space.
To protect yourself and your family from carbon monoxide poisoning, it’s crucial to have your heat exchanger inspected regularly by a qualified professional. They can identify any cracks or leaks in the heat exchanger and take appropriate measures to address the issue. Additionally, installing carbon monoxide detectors in your home is strongly recommended. These detectors can alert you to the presence of carbon monoxide, giving you precious time to evacuate and seek help.
Proper Combustion and Ventilation
Proper combustion and ventilation are essential for the safe operation of a heat exchanger. When the heat exchanger is functioning correctly, it efficiently transfers heat from one fluid to another without any combustion byproducts entering the living space. However, if the combustion process is compromised, such as incomplete burning of fuel, carbon monoxide production can occur.
If you notice a yellow or flickering flame in your gas furnace, it may indicate a problem with the heat exchanger as it may not be properly burning the fuel, leading to poor combustion and the production of carbon monoxide . If you observe any unusual odors, such as a strong metallic or burning smell, coming from your heating system, it’s important to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage or safety risks.
Proper ventilation is also crucial for the safe operation of a heat exchanger. A well-ventilated system ensures that any combustion byproducts, including carbon monoxide, are safely expelled from your home. Make sure that the ventilation system, such as flues and chimneys, is regularly inspected and cleaned to maintain proper airflow.
By prioritizing safety and addressing any potential issues promptly, you can ensure the optimal and safe functioning of your heat exchanger. If you suspect any problems with your heat exchanger, such as increased dust or debris around your furnace or unusual odors, it’s best to consult a qualified HVAC professional to assess and resolve the issue. Don’t compromise on safety when it comes to your heat exchanger.
Types of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers come in various designs, each tailored to specific applications and requirements. Understanding the different types of heat exchangers can help you make informed decisions about heat exchanger maintenance and ensure optimal performance. Let’s explore three common types of heat exchangers: shell and tube heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers, and finned tube heat exchangers.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers are widely used across industries such as power generation, oil and gas refineries, and shipbuilding . This type of heat exchanger consists of a shell (outer vessel) and a bundle of tubes inside. The hot fluid flows through the tubes, while the cold fluid circulates around the tubes in the shell. This design allows for efficient heat transfer between the two fluids.
Shell and tube heat exchangers are known for their versatility and robust construction. They can handle high pressure and temperature differentials, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Additionally, their design allows for easy cleaning and maintenance, contributing to their durability and longevity.
Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are compact and highly efficient, making them popular in HVAC systems, refrigeration, and food processing industries . This type of heat exchanger consists of a series of thin plates with alternating hot and cold fluid channels. The plates create a large surface area for heat transfer, enabling efficient exchange between the fluids.
Plate heat exchangers offer several advantages, including their compact size, high heat transfer rate, and easy maintenance. The removable plates allow for easy access and cleaning, minimizing downtime during maintenance. Moreover, their modular design allows for easy expansion or modification as per changing needs.
Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
Finned tube heat exchangers are designed with extended surfaces, known as fins, on the tubes. These fins increase the heat transfer area and improve efficiency, making them suitable for air conditioning, refrigeration, and heat recovery applications . The heat exchange process takes place as the fluid flows inside the tubes, while air or another fluid passes over the finned surface.
Finned tube heat exchangers are particularly effective in situations where compactness and high heat transfer rates are essential. The fin design enhances heat transfer, allowing for improved performance and energy efficiency. These heat exchangers are commonly used in applications where space is limited or in environments with high heat transfer requirements.
Understanding the characteristics and applications of each type of heat exchanger can help you determine which one is most suitable for your specific needs. Regular heat exchanger maintenance is vital to ensure optimal performance and prevent issues such as fouling, corrosion, and decreased efficiency. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of heat exchangers and their maintenance requirements, you can keep the heat flowing smoothly and efficiently in your system.
Heat Exchanger Maintenance Practices
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your heat exchanger, regular maintenance is essential. By implementing effective maintenance practices, you can prevent common problems, enhance efficiency, and avoid the dangers associated with heat exchanger failure. Here are some proven methods for heat exchanger maintenance.
Annual Inspection and Cleaning
Performing an annual inspection and cleaning is a crucial step in heat exchanger maintenance. Over time, dirt, debris, and fouling can accumulate on the surfaces, hindering heat transfer and decreasing efficiency. Regular cleaning helps to remove these deposits and maintain optimal performance.
During the inspection, check for any signs of fouling, corrosion, or tube leaks. Look for deposits of solid particles or scaling on the inner surface of the tubes, which can significantly reduce heat transfer efficiency and increase energy consumption. If fouling is detected, cleaning the surfaces is necessary to restore efficiency and prevent further issues.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Having a preventive maintenance checklist can ensure that all necessary maintenance tasks are carried out regularly. This checklist should include:
- Cleaning the surfaces to remove debris and fouling, enhancing heat transfer efficiency .
- Inspecting and repairing leaks or damaged seals to prevent product contamination and loss .
- Checking for signs of corrosion and applying protective coatings as necessary .
- Verifying the proper functioning of valves, controls, and safety devices to ensure safe operation.
- Checking for proper fluid flow and pressure, ensuring optimal heat exchange performance.
By following a comprehensive preventive maintenance checklist, you can address potential problems proactively and minimize the risk of heat exchanger failures.
Monitoring Performance and Temperature
Regularly monitoring the performance and temperature of the heat exchanger is crucial for early detection of any issues. Keep an eye on performance indicators such as reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, or inconsistent temperature differentials.
If you observe any significant changes or deviations from normal operation, investigate the cause promptly. Addressing issues in their early stages can prevent further damage and more costly repairs.
Remember to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for specific maintenance procedures and schedules, as they may vary depending on the type and design of the heat exchanger.
By implementing these maintenance practices, you can ensure the optimal performance, efficiency, and safety of your heat exchanger. Regular cleaning, inspection, and monitoring are key to preventing common problems such as fouling, corrosion, and tube leaks. Prioritizing maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the heat exchanger but also minimizes the risk of costly shutdowns and production losses.
For more information on heat exchangers and their maintenance, you can explore our articles on heat exchanger types and heat exchanger cleaning.